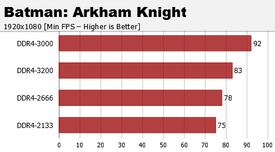
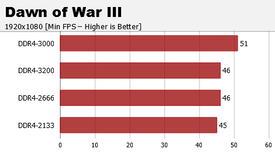
Abbiamo deciso di testare il Core i7-7800X con diverse generazioni di videogiochi, così da capire quanto effettivamente questa nuova microarchitettura, che come abbiamo visto ha rivoluzionato il design della Cache rispetto alle uArch precedenti, sia dipendente dalla frequenza della RAM. In tutti i casi si può notare come una Bandwidth più elevata delle DDR4 porti a prestazioni maggiori, ma non solo. Le RAM a 3000 MHz garantiscono, come abbiamo visto in precedenza, una frequenza più elevata del Mesh Interconnect (Che passa da 800 MHz a 2700 MHz). Questo valore va poi direttamente ad influenzare la velocità della Cache L3, e lo si nota specialmente in Batman: Arkham Knight.
Nella maggior parte dei giochi si nota un aumento minimo dei frame passando dalle RAM a 2133 MHz alle RAM a 3200 MHz (Escludendo le DDR4 @3000MHz), nonostante la Bandwidth aumenti mediamente del 28%. Quando invece è la Cache L3 a subire un notevole Boost, cioè quando le RAM operano a 3000 MHz, l'aumento di frame è molto più elevato. Questo può essere determinato da come sono stati compilati i motori di gioco, i quali fanno riferimento ad un Design che è cambiato in maniera minima da Nehalem, 2009, a Skylake-S/KabyLake, 2017 (Vedere tabella qui in basso). Con Skylake-SP/-X in futuro probabilmente assisteremo a discreti miglioramenti prestazionali, cioè quando i vari sviluppatori si metteranno a patchare i propri motori grafici e fisici per sfruttarne il nuovo design delle CPU Intel (Cache L2 e L3 in primis).
| uArch | Cache L2 | Cache L3 |
| Nehalem (i7-870) | 4 x 256 KB 8-way set associative caches | 8 MB 16-way set associative shared cache |
| Westmere (i7-980) | 6 x 256 KB 8-way set associative caches | 12 MB 16-way set associative shared cache |
| Sandy Bridge (i7-2700K) |
4 x 256 KB 8-way set associative caches | 8 MB 16-way set associative shared cache |
| Sandy Bridge-E (i7-3930K) | 6 x 256 KB 8-way set associative caches | 12 MB 16-way set associative shared cache |
| Ivy Bridge (i7-3770K) | 4 x 256 KB 8-way set associative caches | 8 MB 16-way set associative shared cache |
| Ivy Bridge-E (i7-4930K) | 6 x 256 KB 8-way set associative caches | 12 MB 16-way set associative shared cache |
| Haswell (i7-4790K) | 4 x 256 KB 8-way set associative caches | 8 MB 16-way set associative shared cache |
| Haswell-E (i7-5930K) | 6 x 256 KB 8-way set associative caches | 15 MB 20-way set associative shared cache |
| Broadwell (i7-5775C) | 4 x 256 KB 8-way set associative caches | 6 MB 12-way set associative shared cache |
| Broadwell-E (i7-6900K) | 8 x 256 KB 8-way set associative caches | 15 MB 20-way set associative shared cache |
| Skylake-S (i7-6700K) | 4 x 256 KB 4-way set associative caches | 8 MB 16-way set associative shared cache |
| Skylake-X (i7-7800X) | 6 x 1MB 16-way set associative caches | 8.25 MB 11-way non-inclusive cache |